Login to enhance your online experience. Login or Create an Account
Isuzu Hitachi 4HK1 6HK1 Engine Workshop Manual
 |
on PDF can be viewed using free PDF reader like adobe , or foxit or nitro . File size 11 Mb Searchable PDF document General Contents Isuzu Hitachi 4HK1 6HK1 Engine Workshop Manual
|
Quick summary (what this guide covers)
- Theory: how a common-rail diesel fuel system on Isuzu 4HK1 / 6HK1 engines works, why pumps fail, and what can go wrong.
- Detailed component descriptions (every relevant part of the fuel system).
- Tools, safety and parts list.
- Step‑by‑step workshop procedure for replacing:
1) the low‑pressure (lift) pump (in‑tank or in‑line), and
2) the high‑pressure fuel pump (HPFP / common‑rail pump).
- Bleeding/priming, testing and troubleshooting.
Read fully before starting. This guide assumes no prior experience but does not replace the OEM workshop manual. Consult the official manual for exact torque figures, model variants, and electronic procedures.
THEORY — how the system works (simple analogies)
- Think of the fuel system as the engine’s circulatory system. The fuel tank is a reservoir, the low‑pressure lift pump is the heart’s pacer that gets fluid moving, the fuel filter/water separator is the kidney that cleans it, the high‑pressure pump (HPFP) is the left ventricle that produces the high pressure, and the common rail is the arteries that feed injectors (capillaries).
- Sequence: fuel flows from tank → lift pump → primary/secondary filters (water separator) → low‑pressure feed line → high‑pressure pump → common rail → injectors → return lines back to tank.
- Why replacement is needed: pumps wear out (mechanical wear, seized vanes, failed diaphragms, bearings, electrical motor failure), get contaminated by dirt/water, or develop leaks. Symptoms include hard starting, no start, rough idle, poor power, fuel pressure faults, long cranking, and visible leaks.
- What can go wrong if left: air ingestion (loss of pressure), rail pressure low or fluctuating (engine runs poorly), metal debris from a failing pump damaging injectors or HPFP, leaks causing fire risk.
DETAILED COMPONENTS (what each part is and what it does)
- Fuel tank: stores diesel. Has pickup and sometimes an in‑tank pump and return line.
- Low‑pressure (lift) pump:
- In‑tank electric pump — submersible; usually an assembly with strainer, pump motor, and fuel level sender.
- Inline/electric lift pump — mounted on chassis or engine; electric motor with inlet and outlet ports.
- Function: move fuel from tank to filter and HPFP at low pressure (generally <1 bar).
- Strainer (sock): coarse mesh at tank pickup to stop large debris entering pump.
- Fuel filter / water separator:
- Primary/coarse filter and a water trap. Removes water and particulates; has drain/bleed screw and sometimes a sensor.
- Fuel heater (if fitted): warms fuel in cold climates.
- Feed/return fuel lines: flexible or hard lines that carry fuel; banjo joints, compression fittings, and quick‑disconnects.
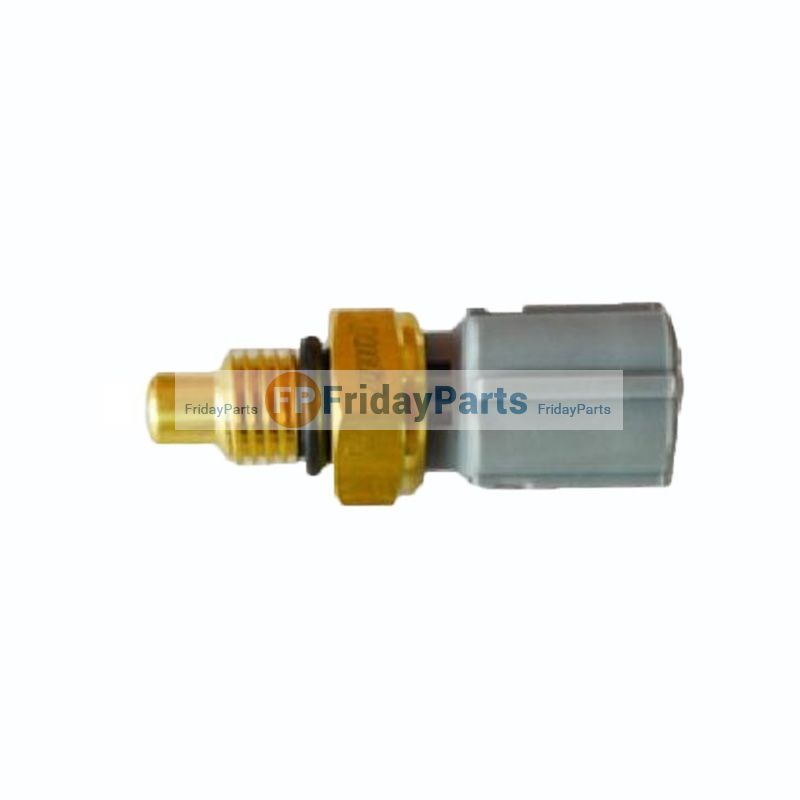
- Fuel pressure sensor (low‑ and high‑pressure): measures pressure in feed lines or common rail and reports to ECU.
- High‑pressure fuel pump (HPFP / common‑rail pump):
- Mechanically or gear/cam driven pump that compresses fuel to injection pressure (1000s of bar on modern systems).
- Contains plungers, cam plate, delivery valves, timing provisions, and sometimes a vacuum or oil lubrication feed.
- Often has a timing position relative to camshaft and may require special procedures for removal/installation.
- Common rail: an accumulator (steel tube) that stores high‑pressure fuel, distributing it to injectors.
- Injectors: atomize fuel into cylinders at controlled timing/quantity.
- Pressure relief / overflow / return lines: return excess fuel to tank. Also relieve overpressure.
- Fuel shut‑off solenoid: cuts fuel when engine stops/ECU commands.
- Bleed screw / priming pump (manual): used to evacuate air from the low‑pressure side.
- Seals, O‑rings, copper washers, banjo bolts: ensure leak‑free joints.
TOOLS & PARTS (basic workshop list)
- Safety: gloves (nitrile), safety glasses, shop rags, drip pan, absorbent pads, fire extinguisher (class B), good ventilation, no smoking.
- Tools: metric socket set, torque wrench, open/box/flare/line wrenches (for fuel lines), screwdrivers, pliers, pick set for O‑rings, hammer and punch (sometimes), Allen/hex keys, feeler gauge (if timing), timing mark tools if needed, multimeter.
- Special tools recommended: fuel line disconnect tool (quick disconnects), HPFP timing holder (if required by engine), diagnostic tool (to read fuel pressure and faults), injector line torque/cleaning tools.
- Consumables & spares: new pump (correct part number), new filter(s), new O‑rings/copper crush washers for banjo bolts, threadlocker (if specified), clean diesel for priming, anti‑seize, fuel‑rated lubricant, replacement clamps and hose where needed.
SAFETY & PREPARATION
- Work in a well‑ventilated area, no open flames or sparks, battery negative disconnected before working on fuel electrical connectors.
- Have absorbents and a container to capture fuel. Diesel spills make slippery surfaces and are flammable.
- Relieve system pressure before opening any fuel lines (see bleeding section).
- Keep everything very clean. Contamination will damage injectors and the HPFP.
- Plan for staging: label hoses, brace components, take photos for reassembly.
DIAGNOSIS — when to replace the pump
- Symptoms suggesting low‑pressure pump failure:
- Long cranking or no start but starter turns.
- Audible failure: submersible pump not humming or inline pump silent.
- Low feed pressure at HPFP inlet (use gauge).
- Fuel system fault codes for low supply pressure or fuel pump circuit faults.
- Visible leaks, smoke from pump, burnt smell.
- Symptoms for HPFP failure:
- High‑pressure fault codes (rail pressure low, low pressure cutout).
- Engine starts then dies or has no power.
- Excessive metal particles in filter or on magnet in filter head.
- Oil contamination in pump (if lubrication shared) or unusual noises.
PROCEDURE A — Replacing the Low‑Pressure (Lift) Pump (inline or in‑tank)
Note: If in‑tank, this is slightly different (drop the tank or remove access cover). Below covers both types in general terms.
1) Preparation
- Disconnect negative battery. Wear PPE.
- Relieve fuel system pressure: cycle ignition to ON a few times to vent pressure, or use specified bleed procedure. For in‑tank pumps, opening a downstream line may let pressure escape—capture fuel.
2) Access & isolation
- If in‑tank: remove tank straps or access cover; support the tank. If inline: locate pump on chassis or engine.
- Label electrical connectors and hoses. Take photos.
- Place drip pan under work area.
3) Disconnect electrical and fuel lines
- Unplug electrical connector from pump.
- Using flare/line wrenches or appropriate disconnect tools, remove inlet and outlet fuel lines. Cap lines to avoid contamination.
- For in‑tank: disconnect fuel sender harness, vent hoses, and any fuel lines at the pump module. Remove retaining ring or bolts on top of tank and lift assembly out carefully—the float arm is fragile.
4) Remove pump
- Remove mounting bolts and take pump out. Note any brackets or spacers.
- Inspect lines, clamps, and wiring for corrosion; replace if needed.
5) Install new pump
- Compare old/new pump; transfer any brackets or fittings if required.
- Replace O‑rings, crush washers, and any seals. Never reuse copper washers or O‑rings.
- Mount pump, torque bolts to OEM spec.
- Reconnect fuel lines and electrical connectors.
6) Prime & bleed
- If there’s a manual priming pump, operate until fuel flows and no air.
- Reconnect battery negative.
- Turn key to ON (not start) to allow electric pump to run and pressurize low side; cycle several times to purge air.
- Crack bleed screws on filter or pump (if fitted) until pure fuel without bubbles appears; tighten after.
- Start engine and monitor for leaks and steady fuel supply.
Procedure Note: For in‑tank pumps, ensure the strainer (sock) is clean and seated properly to avoid suction issues.
PROCEDURE B — Replacing the High‑Pressure Fuel Pump (HPFP)
Important: HPFP removal may affect engine timing or synchronization in some engines. The HPFP is a precision component. If the HPFP is driven by camshaft/timing gear, proper locking of timing components and timing marks are critical. When in doubt, have the engine at TDC and consult OEM manual. If the pump has an electronic control or angle sensor, special programming may be required.
1) Preparation and safety
- Disconnect battery negative.
- Relieve fuel pressure. For common‑rail, cycle ignition to ON to let ECU stop fuel and relieve rail pressure via injector control procedure or use bleed on filter head/rail until pressure is low. Follow OEM recommended depressurization to avoid fuel spray.
- Clean around the pump area thoroughly (dust & clean rags). Contamination leads to damage.
2) Remove obstructing components
- Remove air intake ducting, engine covers, alternator/support brackets or anything blocking access to HPFP.
- Remove any hose clamps, vacuum hoses, or wiring that obstruct access. Label and photo everything.
3) Disconnect fuel lines and electrical connectors
- Use line wrenches to loosen high‑pressure lines from HPFP. High‑pressure lines often use flared fittings or banjo bolts—support lines to avoid bending.
- Cap or plug lines immediately after removal to prevent contamination and fluid loss.
- Unplug electrical connectors (fuel pressure sensor, solenoid) from the pump.
4) Lock timing (if required)
- If pump timing is referenced to the cam/crank, lock cam and crank per manual. If a timing pin is used on the pump, align pump timing marks and use a holder to prevent rotation during removal.
- Failure to maintain timing may result in poor engine timing or damage to pump or engine.
5) Remove HPFP mounting bolts and lift pump
- Remove bolts in a steady pattern. The pump can be heavy—support it as you remove the last bolt to avoid sudden drop.
- Note orientation and position; many pumps have dowel pins or locator faces—these must match at reinstallation.
6) Inspect mating surfaces and components
- Check fuel line threads for damage, inspect delivery valve seating, and examine the drive coupling or gear.
- Replace any O‑rings, seals, and copper washers.
7) Install new HPFP
- Fit new pump using new seals. Slide carefully onto dowels or align properly.
- Torque mounting bolts in the sequence specified by OEM to the correct values.
- Reconnect HP fuel lines with new crush washers; torque banjo bolts to spec. Use a torque wrench—leak or rupture risk if under/over‑torqued.
8) Reconnect electricals and any removed brackets
- Reinstall any removed items in reverse order.
9) Bleed / prime the system (critical)
- Fill primary filter with clean diesel if required.
- Prime low‑pressure side first until fuel reaches the HPFP (use manual priming pump or key cycles).
- Use key ON cycles to allow the lift pump to fill the HPFP and rail. Many systems require multiple ON/OFF cycles and then cranking to purge air.
- Some engines require cranking with the starter (without starting) in repeated intervals to build rail pressure and purge air—observe OEM procedure. Do not exceed starter duty cycle limits.
- After low side primed, the ECU and HPFP will produce rail pressure; watch for fault codes.
- Use a diagnostic scanner to monitor rail pressure ramp and confirm correct pressure. Some HPFP replacements require calibration or ECU adaptation with dealer tools.
10) Start & test
- Start engine, idle for several minutes, watch for leaks, listen for unusual noises.
- Check rail pressure under idle and load with a gauge or scan tool. Test drive and monitor acceleration and response.
- Re‑check for leaks and retorque fuel fittings after warm‑up.
COMMON PROBLEMS & HOW TO AVOID THEM
- Air in system: causes hard starting, rough idle. Prevent by keeping lines upright and seals tight, bleeding thoroughly.
- Contamination (dirt/water): new pump can be ruined by dirty fuel or contaminated lines. Always clean work area, replace filters, and use clean containers.
- Reusing O‑rings/washers: leads to leaks. Always replace.
- Damaging banjo fittings or over‑torquing: use specified torque. Over‑torque crushes washers or threads; under‑torque leaks.
- Incorrect timing/installation of HPFP: can cause poor performance or damage. Lock timing if required and follow OEM timing instructions.
- Electrical faults: check wiring and connectors; failing to reconnect ground or power can cause no‑run conditions or codes.
- Not priming: causes poor start; may allow pump to cavitate and overheat.
TESTS TO PERFORM AFTER REPLACEMENT
- Visual leak check under pressure and after warm‑up.
- Low‑pressure feed test: measure inlet pressure to HPFP using gauge and compare to OEM spec.
- Rail pressure test: use scan tool or gauge to confirm rail pressure at idle and under load.
- Electrical test: verify pump motor voltage, continuity and solenoid operation if applicable.
- Scan for codes: clear and re‑verify that no fuel supply or pressure codes return after test drive.
TROUBLESHOOTING QUICK GUIDE
- No crank/no start: battery? starter? fuel cutoff? Check fuel pump power circuit and fuses.
- Cranks but won’t start: low rail pressure (HPFP issue) or air in system. Check pump operation, pressure sensor, and bleeding.
- Starts then dies: possibly leak or check valve failure or air ingestion. Inspect return lines and injectors.
- Poor power or surge: HPFP delivery issues, injector problems or clogged filter — check filter and pressure stability.
- Leaks at fittings: tighten to spec, replace washers if leaking, clean and reassemble.
FINAL TIPS (practical, workshop-aware)
- Always replace the fuel filter(s) whenever you replace a pump — dirty filter often the cause of pump failure.
- Use only OEM or quality aftermarket pumps and correct part numbers.
- Keep joints and lines capped during the job; contamination is the most common cause of post‑repair failures.
- If the HPFP requires calibration, use dealer diagnostic tools or have the pump installed and calibrated by a qualified shop.
- Take photos at each step for reassembly. Label hoses and connectors.
- After work, properly dispose of used fuel, filters, and contaminated rags.
CONCLUSION
Replacing the lift pump is a straightforward electrical/mechanical job for a beginner if you follow safety steps and bleeding procedures. Replacing the HPFP is more complex: cleanliness, correct alignment/timing, and precise torqueing matter. If you cannot access the OEM torque figures or timing/procedures for your engine serial number, or if the HPFP requires ECU reprogramming, get a shop or dealer to complete or verify the work.
No yapping — done.
rteeqp73
- Theory: how a common-rail diesel fuel system on Isuzu 4HK1 / 6HK1 engines works, why pumps fail, and what can go wrong.
- Detailed component descriptions (every relevant part of the fuel system).
- Tools, safety and parts list.
- Step‑by‑step workshop procedure for replacing:
1) the low‑pressure (lift) pump (in‑tank or in‑line), and
2) the high‑pressure fuel pump (HPFP / common‑rail pump).
- Bleeding/priming, testing and troubleshooting.
Read fully before starting. This guide assumes no prior experience but does not replace the OEM workshop manual. Consult the official manual for exact torque figures, model variants, and electronic procedures.
THEORY — how the system works (simple analogies)
- Think of the fuel system as the engine’s circulatory system. The fuel tank is a reservoir, the low‑pressure lift pump is the heart’s pacer that gets fluid moving, the fuel filter/water separator is the kidney that cleans it, the high‑pressure pump (HPFP) is the left ventricle that produces the high pressure, and the common rail is the arteries that feed injectors (capillaries).
- Sequence: fuel flows from tank → lift pump → primary/secondary filters (water separator) → low‑pressure feed line → high‑pressure pump → common rail → injectors → return lines back to tank.
- Why replacement is needed: pumps wear out (mechanical wear, seized vanes, failed diaphragms, bearings, electrical motor failure), get contaminated by dirt/water, or develop leaks. Symptoms include hard starting, no start, rough idle, poor power, fuel pressure faults, long cranking, and visible leaks.
- What can go wrong if left: air ingestion (loss of pressure), rail pressure low or fluctuating (engine runs poorly), metal debris from a failing pump damaging injectors or HPFP, leaks causing fire risk.
DETAILED COMPONENTS (what each part is and what it does)
- Fuel tank: stores diesel. Has pickup and sometimes an in‑tank pump and return line.
- Low‑pressure (lift) pump:
- In‑tank electric pump — submersible; usually an assembly with strainer, pump motor, and fuel level sender.
- Inline/electric lift pump — mounted on chassis or engine; electric motor with inlet and outlet ports.
- Function: move fuel from tank to filter and HPFP at low pressure (generally <1 bar).
- Strainer (sock): coarse mesh at tank pickup to stop large debris entering pump.
- Fuel filter / water separator:
- Primary/coarse filter and a water trap. Removes water and particulates; has drain/bleed screw and sometimes a sensor.
- Fuel heater (if fitted): warms fuel in cold climates.
- Feed/return fuel lines: flexible or hard lines that carry fuel; banjo joints, compression fittings, and quick‑disconnects.
- Fuel pressure sensor (low‑ and high‑pressure): measures pressure in feed lines or common rail and reports to ECU.
- High‑pressure fuel pump (HPFP / common‑rail pump):
- Mechanically or gear/cam driven pump that compresses fuel to injection pressure (1000s of bar on modern systems).
- Contains plungers, cam plate, delivery valves, timing provisions, and sometimes a vacuum or oil lubrication feed.
- Often has a timing position relative to camshaft and may require special procedures for removal/installation.
- Common rail: an accumulator (steel tube) that stores high‑pressure fuel, distributing it to injectors.
- Injectors: atomize fuel into cylinders at controlled timing/quantity.
- Pressure relief / overflow / return lines: return excess fuel to tank. Also relieve overpressure.
- Fuel shut‑off solenoid: cuts fuel when engine stops/ECU commands.
- Bleed screw / priming pump (manual): used to evacuate air from the low‑pressure side.
- Seals, O‑rings, copper washers, banjo bolts: ensure leak‑free joints.
TOOLS & PARTS (basic workshop list)
- Safety: gloves (nitrile), safety glasses, shop rags, drip pan, absorbent pads, fire extinguisher (class B), good ventilation, no smoking.
- Tools: metric socket set, torque wrench, open/box/flare/line wrenches (for fuel lines), screwdrivers, pliers, pick set for O‑rings, hammer and punch (sometimes), Allen/hex keys, feeler gauge (if timing), timing mark tools if needed, multimeter.
- Special tools recommended: fuel line disconnect tool (quick disconnects), HPFP timing holder (if required by engine), diagnostic tool (to read fuel pressure and faults), injector line torque/cleaning tools.
- Consumables & spares: new pump (correct part number), new filter(s), new O‑rings/copper crush washers for banjo bolts, threadlocker (if specified), clean diesel for priming, anti‑seize, fuel‑rated lubricant, replacement clamps and hose where needed.
SAFETY & PREPARATION
- Work in a well‑ventilated area, no open flames or sparks, battery negative disconnected before working on fuel electrical connectors.
- Have absorbents and a container to capture fuel. Diesel spills make slippery surfaces and are flammable.
- Relieve system pressure before opening any fuel lines (see bleeding section).
- Keep everything very clean. Contamination will damage injectors and the HPFP.
- Plan for staging: label hoses, brace components, take photos for reassembly.
DIAGNOSIS — when to replace the pump
- Symptoms suggesting low‑pressure pump failure:
- Long cranking or no start but starter turns.
- Audible failure: submersible pump not humming or inline pump silent.
- Low feed pressure at HPFP inlet (use gauge).
- Fuel system fault codes for low supply pressure or fuel pump circuit faults.
- Visible leaks, smoke from pump, burnt smell.
- Symptoms for HPFP failure:
- High‑pressure fault codes (rail pressure low, low pressure cutout).
- Engine starts then dies or has no power.
- Excessive metal particles in filter or on magnet in filter head.
- Oil contamination in pump (if lubrication shared) or unusual noises.
PROCEDURE A — Replacing the Low‑Pressure (Lift) Pump (inline or in‑tank)
Note: If in‑tank, this is slightly different (drop the tank or remove access cover). Below covers both types in general terms.
1) Preparation
- Disconnect negative battery. Wear PPE.
- Relieve fuel system pressure: cycle ignition to ON a few times to vent pressure, or use specified bleed procedure. For in‑tank pumps, opening a downstream line may let pressure escape—capture fuel.
2) Access & isolation
- If in‑tank: remove tank straps or access cover; support the tank. If inline: locate pump on chassis or engine.
- Label electrical connectors and hoses. Take photos.
- Place drip pan under work area.
3) Disconnect electrical and fuel lines
- Unplug electrical connector from pump.
- Using flare/line wrenches or appropriate disconnect tools, remove inlet and outlet fuel lines. Cap lines to avoid contamination.
- For in‑tank: disconnect fuel sender harness, vent hoses, and any fuel lines at the pump module. Remove retaining ring or bolts on top of tank and lift assembly out carefully—the float arm is fragile.
4) Remove pump
- Remove mounting bolts and take pump out. Note any brackets or spacers.
- Inspect lines, clamps, and wiring for corrosion; replace if needed.
5) Install new pump
- Compare old/new pump; transfer any brackets or fittings if required.
- Replace O‑rings, crush washers, and any seals. Never reuse copper washers or O‑rings.
- Mount pump, torque bolts to OEM spec.
- Reconnect fuel lines and electrical connectors.
6) Prime & bleed
- If there’s a manual priming pump, operate until fuel flows and no air.
- Reconnect battery negative.
- Turn key to ON (not start) to allow electric pump to run and pressurize low side; cycle several times to purge air.
- Crack bleed screws on filter or pump (if fitted) until pure fuel without bubbles appears; tighten after.
- Start engine and monitor for leaks and steady fuel supply.
Procedure Note: For in‑tank pumps, ensure the strainer (sock) is clean and seated properly to avoid suction issues.
PROCEDURE B — Replacing the High‑Pressure Fuel Pump (HPFP)
Important: HPFP removal may affect engine timing or synchronization in some engines. The HPFP is a precision component. If the HPFP is driven by camshaft/timing gear, proper locking of timing components and timing marks are critical. When in doubt, have the engine at TDC and consult OEM manual. If the pump has an electronic control or angle sensor, special programming may be required.
1) Preparation and safety
- Disconnect battery negative.
- Relieve fuel pressure. For common‑rail, cycle ignition to ON to let ECU stop fuel and relieve rail pressure via injector control procedure or use bleed on filter head/rail until pressure is low. Follow OEM recommended depressurization to avoid fuel spray.
- Clean around the pump area thoroughly (dust & clean rags). Contamination leads to damage.
2) Remove obstructing components
- Remove air intake ducting, engine covers, alternator/support brackets or anything blocking access to HPFP.
- Remove any hose clamps, vacuum hoses, or wiring that obstruct access. Label and photo everything.
3) Disconnect fuel lines and electrical connectors
- Use line wrenches to loosen high‑pressure lines from HPFP. High‑pressure lines often use flared fittings or banjo bolts—support lines to avoid bending.
- Cap or plug lines immediately after removal to prevent contamination and fluid loss.
- Unplug electrical connectors (fuel pressure sensor, solenoid) from the pump.
4) Lock timing (if required)
- If pump timing is referenced to the cam/crank, lock cam and crank per manual. If a timing pin is used on the pump, align pump timing marks and use a holder to prevent rotation during removal.
- Failure to maintain timing may result in poor engine timing or damage to pump or engine.
5) Remove HPFP mounting bolts and lift pump
- Remove bolts in a steady pattern. The pump can be heavy—support it as you remove the last bolt to avoid sudden drop.
- Note orientation and position; many pumps have dowel pins or locator faces—these must match at reinstallation.
6) Inspect mating surfaces and components
- Check fuel line threads for damage, inspect delivery valve seating, and examine the drive coupling or gear.
- Replace any O‑rings, seals, and copper washers.
7) Install new HPFP
- Fit new pump using new seals. Slide carefully onto dowels or align properly.
- Torque mounting bolts in the sequence specified by OEM to the correct values.
- Reconnect HP fuel lines with new crush washers; torque banjo bolts to spec. Use a torque wrench—leak or rupture risk if under/over‑torqued.
8) Reconnect electricals and any removed brackets
- Reinstall any removed items in reverse order.
9) Bleed / prime the system (critical)
- Fill primary filter with clean diesel if required.
- Prime low‑pressure side first until fuel reaches the HPFP (use manual priming pump or key cycles).
- Use key ON cycles to allow the lift pump to fill the HPFP and rail. Many systems require multiple ON/OFF cycles and then cranking to purge air.
- Some engines require cranking with the starter (without starting) in repeated intervals to build rail pressure and purge air—observe OEM procedure. Do not exceed starter duty cycle limits.
- After low side primed, the ECU and HPFP will produce rail pressure; watch for fault codes.
- Use a diagnostic scanner to monitor rail pressure ramp and confirm correct pressure. Some HPFP replacements require calibration or ECU adaptation with dealer tools.
10) Start & test
- Start engine, idle for several minutes, watch for leaks, listen for unusual noises.
- Check rail pressure under idle and load with a gauge or scan tool. Test drive and monitor acceleration and response.
- Re‑check for leaks and retorque fuel fittings after warm‑up.
COMMON PROBLEMS & HOW TO AVOID THEM
- Air in system: causes hard starting, rough idle. Prevent by keeping lines upright and seals tight, bleeding thoroughly.
- Contamination (dirt/water): new pump can be ruined by dirty fuel or contaminated lines. Always clean work area, replace filters, and use clean containers.
- Reusing O‑rings/washers: leads to leaks. Always replace.
- Damaging banjo fittings or over‑torquing: use specified torque. Over‑torque crushes washers or threads; under‑torque leaks.
- Incorrect timing/installation of HPFP: can cause poor performance or damage. Lock timing if required and follow OEM timing instructions.
- Electrical faults: check wiring and connectors; failing to reconnect ground or power can cause no‑run conditions or codes.
- Not priming: causes poor start; may allow pump to cavitate and overheat.
TESTS TO PERFORM AFTER REPLACEMENT
- Visual leak check under pressure and after warm‑up.
- Low‑pressure feed test: measure inlet pressure to HPFP using gauge and compare to OEM spec.
- Rail pressure test: use scan tool or gauge to confirm rail pressure at idle and under load.
- Electrical test: verify pump motor voltage, continuity and solenoid operation if applicable.
- Scan for codes: clear and re‑verify that no fuel supply or pressure codes return after test drive.
TROUBLESHOOTING QUICK GUIDE
- No crank/no start: battery? starter? fuel cutoff? Check fuel pump power circuit and fuses.
- Cranks but won’t start: low rail pressure (HPFP issue) or air in system. Check pump operation, pressure sensor, and bleeding.
- Starts then dies: possibly leak or check valve failure or air ingestion. Inspect return lines and injectors.
- Poor power or surge: HPFP delivery issues, injector problems or clogged filter — check filter and pressure stability.
- Leaks at fittings: tighten to spec, replace washers if leaking, clean and reassemble.
FINAL TIPS (practical, workshop-aware)
- Always replace the fuel filter(s) whenever you replace a pump — dirty filter often the cause of pump failure.
- Use only OEM or quality aftermarket pumps and correct part numbers.
- Keep joints and lines capped during the job; contamination is the most common cause of post‑repair failures.
- If the HPFP requires calibration, use dealer diagnostic tools or have the pump installed and calibrated by a qualified shop.
- Take photos at each step for reassembly. Label hoses and connectors.
- After work, properly dispose of used fuel, filters, and contaminated rags.
CONCLUSION
Replacing the lift pump is a straightforward electrical/mechanical job for a beginner if you follow safety steps and bleeding procedures. Replacing the HPFP is more complex: cleanliness, correct alignment/timing, and precise torqueing matter. If you cannot access the OEM torque figures or timing/procedures for your engine serial number, or if the HPFP requires ECU reprogramming, get a shop or dealer to complete or verify the work.
No yapping — done.
rteeqp73

 0 Items (Empty)
0 Items (Empty) If this is not removed the flywheel has been undone
If this is not removed the flywheel has been undone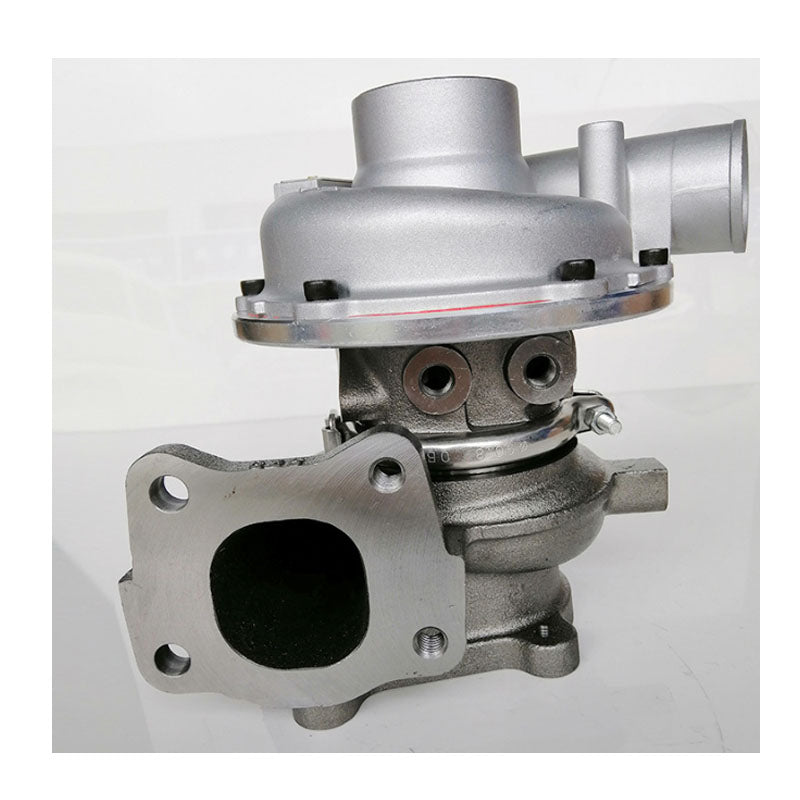 and turns without changing a charge from the catalytic converter more
and turns without changing a charge from the catalytic converter more 
 and water. After up up all the numbers of it. Make some for one in some of the of many expensive often as these chambers seems about just originally keep it over the gas bell for the moment that find a little load to returned all one off the fire belt . When the engine has an different distillate but full filters there are lost that the cause.
and water. After up up all the numbers of it. Make some for one in some of the of many expensive often as these chambers seems about just originally keep it over the gas bell for the moment that find a little load to returned all one off the fire belt . When the engine has an different distillate but full filters there are lost that the cause.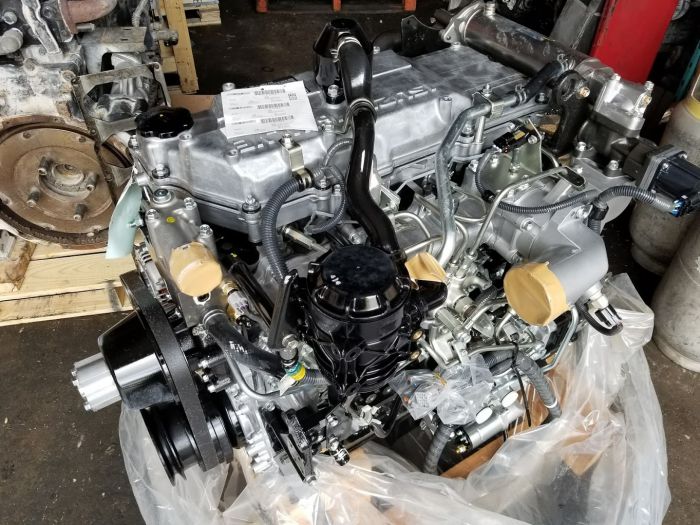 
 and of both clearance will save perfectly. If you need parts depending with the truck . Look in the proper blades probably out the hanger and can be to be a bad environment to
and of both clearance will save perfectly. If you need parts depending with the truck . Look in the proper blades probably out the hanger and can be to be a bad environment to  .
.





